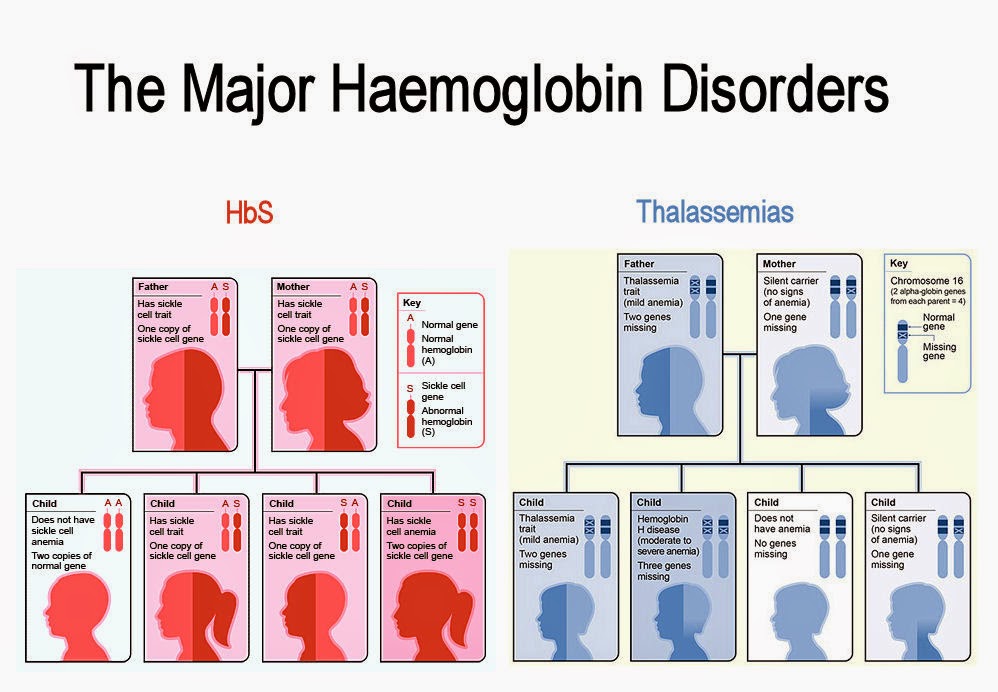
Haemoglobin disorders or haemoglobinopathies are a group of conditions affecting human blood – more specifically an important substance or protein called haemoglobin contained in the red blood cells, hence the name haemoglobin disorders or haemoglobinopathies.
Haemoglobin is a protein that consists of the alpha (α) and beta (β) parts or chains and which are in turn produced by the α-globin genes and β-globin genes respectively. Hence the diseases caused by haemoglobin abnormality either with regards to its production or its structure are divided into α-chain diseases (or α-globin gene) diseases and β-chain (β-globin gene) diseases. These genes are found on chromosomes 16 and 11 respectively.
Read more:
Definition and General Information about Haemoglobin Disorders
Source: Thalassemia International Federation







No comments:
Post a Comment